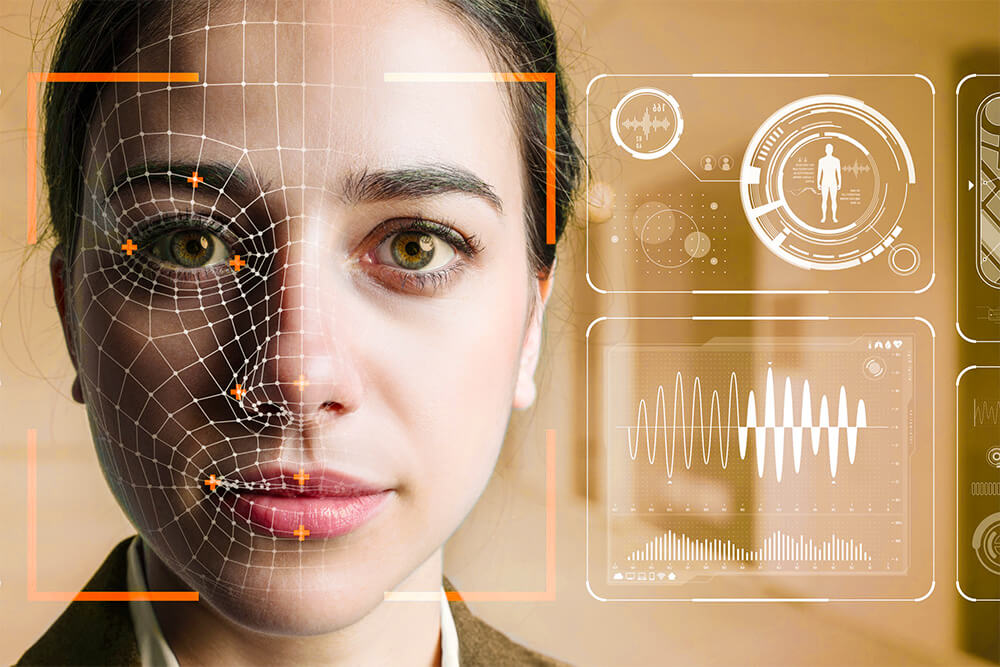
Noun
- Emotion AI (EAI) refers to the ability of machines and systems to recognize, understand, and respond to human emotions.
Synonyms
Emotion AI, Affective computing
Etymology
EAI is an acronym for “Emotional Artificial Intelligence”
The term dates back to 1995 when researcher Rosalind Picard published “Affective Computing“.
The term is derived from the field of artificial intelligence (AI), which involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Emotional AI specifically refers to the capacity of machines to comprehend and react to human emotions, and is based on research in the fields of psychology, neuroscience, and computer science.
Related terms
Artificial intelligence – Human-robot interaction – Machine learning – Natural language processing – Sentiment analysis – Roboethics
Questions
What is the goal of EAI?
The goal of EAI is to enable machines and systems to recognize, understand, and respond to human emotions, in order to improve human-machine interactions and enable more natural and intuitive communication.
What are some examples of applications that use EAI?
Examples of applications that use EAI include virtual assistants, chatbots, and robots that interact with humans. EAI can also be used in fields such as healthcare, where it can be used to help diagnose and treat mental health conditions, and education, where it can be used to personalize learning experiences based on students’ emotional responses.
Read more about the future of EAI
How does EAI work?
EAI works by using machine learning algorithms to analyze data from sensors and other sources, such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language, to identify and classify human emotions. The system can then use this information to tailor its responses to better meet the needs and preferences of the user.
What are some challenges associated with developing EAI?
Some challenges associated with developing EAI include the complexity of human emotions and the variability in how individuals express and experience emotions. Additionally, there are ethical and privacy concerns associated with collecting and using personal data related to emotions.