The world of agriculture is constantly evolving and new technologies play an increasingly important role in shaping our future.
Advances in robotics and artificial intelligence have opened up new possibilities for improving agricultural productivity, efficiency and sustainability.
With a growing world population and increased demand for food, the agricultural industry is facing significant challenges in meeting these needs while maintaining environmentally responsible practices.
Agribots offers a promising solution, enabling farmers to optimize crop management, reduce waste and improve yields.

The use of robots in agriculture is not a new concept, but recent advances in technology have ushered in a new era of innovation and transformation.
From drones to autonomous tractors, the range of robotic applications in agriculture is expanding rapidly.
The agricultural robot market is expected to grow from around 6 Billion in 2021 to 94 Billion (USD) in 2030.
According to Verified Market Research
The main reasons driving the agribot market are the scarcity of skilled labor in the fields, ever higher wages, the need to increase the productivity and quality of crops and increasingly restrictive regulations on the use of pesticides.
The advantages of robotics in agriculture: Efficiency, Productivity and Sustainability
By automating many of the labour-intensive tasks involved in crop management, robots can save time and resources, allowing farmers to focus on other important aspects of their business.

Efficiency is a key benefit of agribots, which can work around the clock, without the need for breaks or rests, enabling farmers to maximize production and minimize downtime. They can also perform tasks with greater precision and accuracy than humans, reducing the risk of errors and waste.
Robotics can increase productivity by improving crop yield and quality. Agribots can monitor crop growth and health in real time, identifying problems early and enabling farmers to take corrective action. This can lead to higher yields and better quality produce.

Sustainability is another major benefit of robotics in agriculture. The integration of agribots can help optimize the use of resources such as water, energy and chemicals, such as fertilizers and pesticides, reducing the environmental impact of agriculture and avoiding harm to human health.
In general, the benefits of robotics in agriculture are numerous and their integration is becoming increasingly important for farmers who want to remain competitive in a rapidly changing sector.
Application typologies of Agribots
Types of robots or drones used in agriculture are:
AG Drone to monitor fields: creating detailed maps of crop health and growth
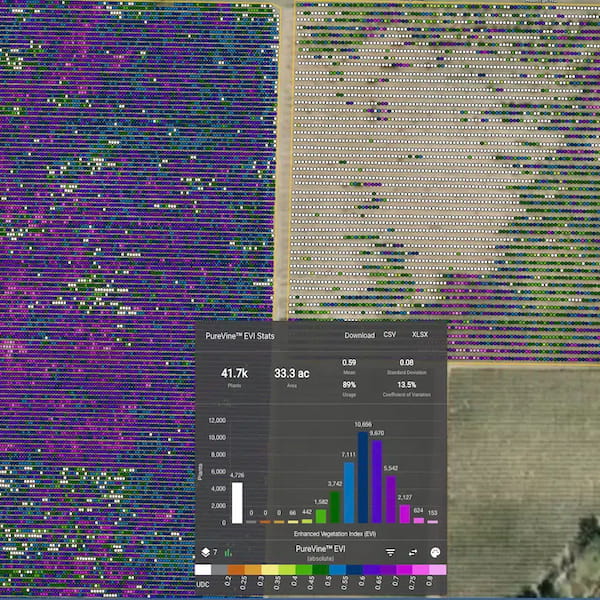
- Vineview: Agribot drone for crop diagnostics for vineyards health.

- Ageagle eBee Ag: UAV captures data to gain greater crop insights to accurately plan and manage operations throughout the growing season.
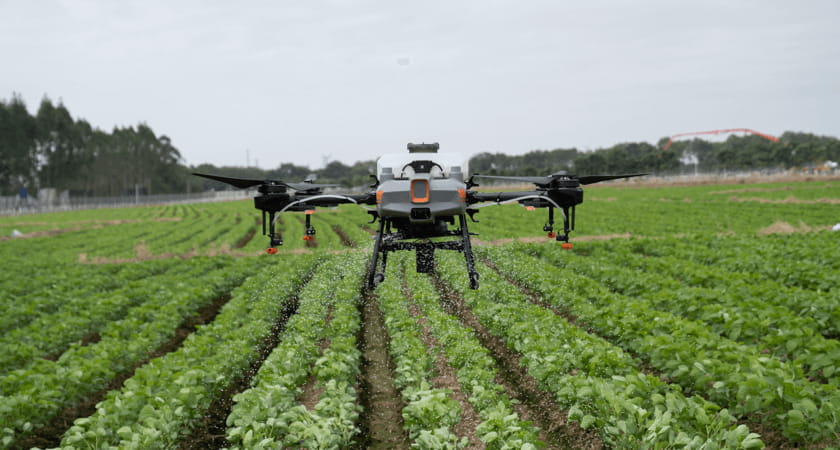

- DJI Agras T10: Agricultural drone for spraying fields for growth cycles and crop health.
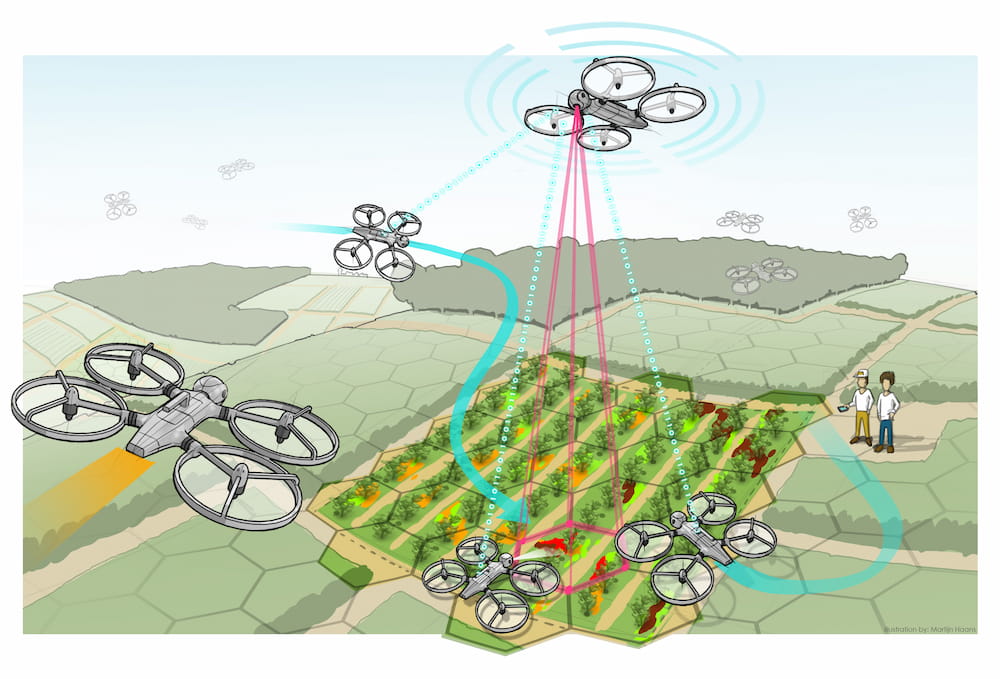
- SAGA: Swarm robotics, swarm agribot drone in particular, is considered extremely relevant for precision farming and large-scale agricultural applications.
Agribot for land management: ploughing, seedbed preparation, seeding or fertilization
- Small Robot Company: Features a family of farming robots, including Tom (crop monitoring), Dick (crop care) and Harry (seeding), who work together to optimize crop management.
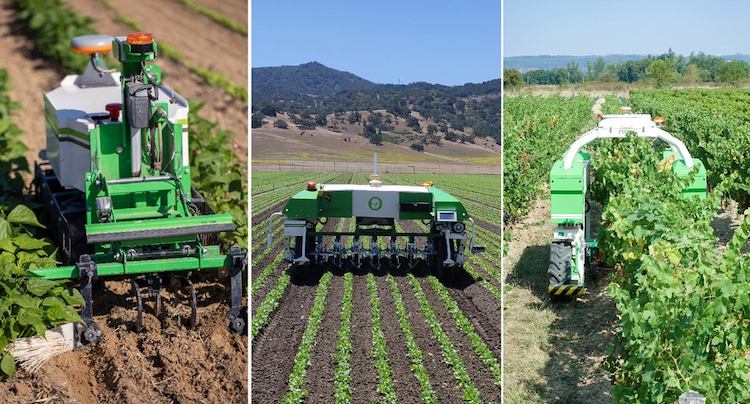

- Naïo Technologies: offers several robots for planting, weeding and harvesting vegetables and vineyards.
- Rowbot: An autonomous robot designed to work between rows of crops such as corn, applying fertilizers and other chemicals in a precise and targeted way.
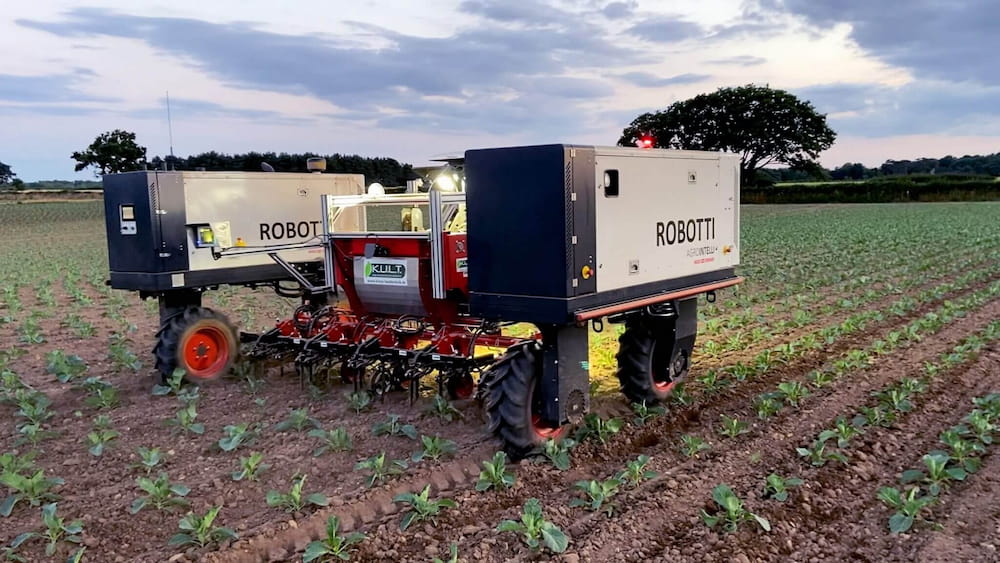

- Agrointelli ROBOTTI LR: an UGV that facilitates automatic data collection, management and decision support in the agricultural sector
- Fendt Xaver: a modular precision seeding robot system that works in a coordinated manner to plant seeds efficiently and accurately.
Agribot for cleaning fields: remove weeds or debris from fields using brushes, lasers or water jets
- Carbon Robotics: removes weeds through lasers
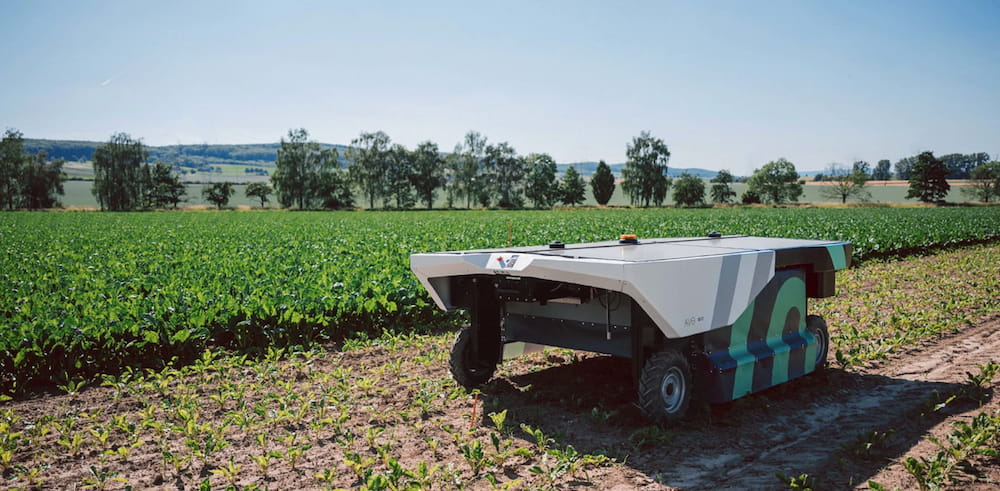

- EcoRobotix Avo: a solar autonomous robot treat up to 10 hectares a day, by using up to 95% less weedkillers.
Agribot for accurate and controlled pruning
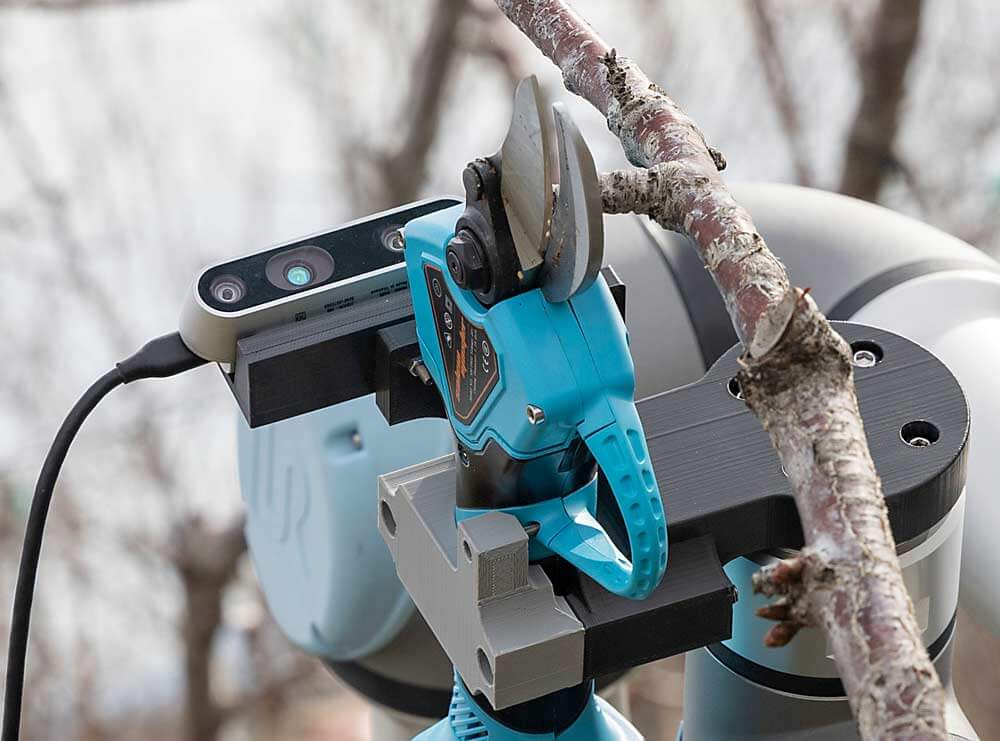

-
Research agribot: The first robot equipped with AI for winter pruning of vineyards and is the result of a research activity conducted by students at Washington State University and Oregon State University
Agribot for the collection of agricultural products
Such as fruit, vegetables or cereals without damaging them, thanks also to the soft grippers.
- FFRobotics: Agri robot that harvests fruit in a unique and patented way efficiently, economically and without bruises.

- Harvest CROO Robotics: strawberry picking farming robot that uses computer vision and artificial intelligence to harvest strawberries efficiently and gently.
- Agrobot: A strawberry picking robot that uses computer vision to pick only ripe strawberries.
Agribot for farm management: feed, milk and clean livestock automatically.
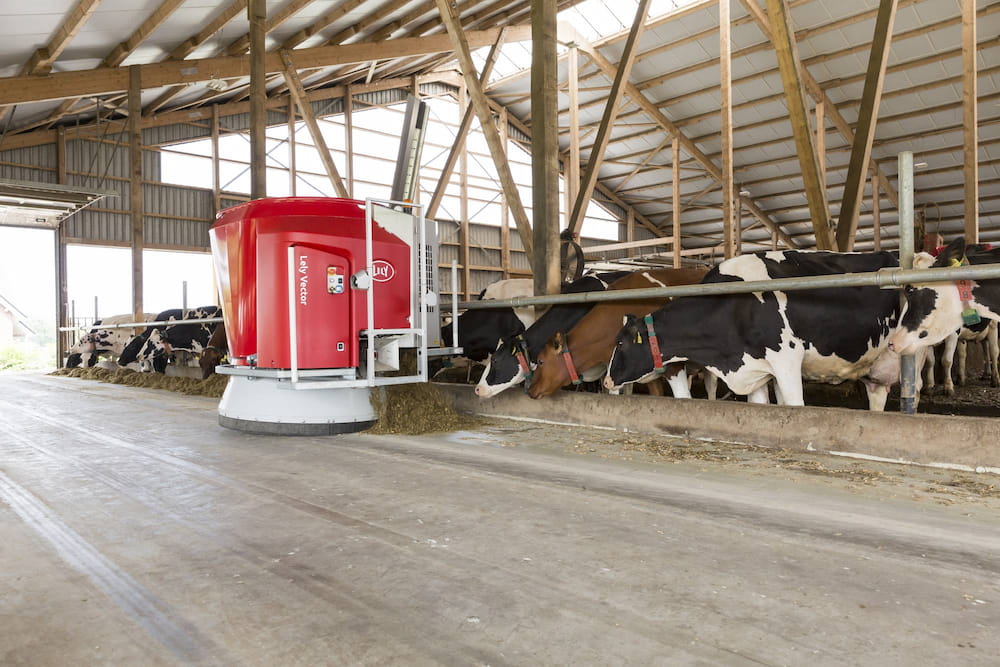

- LELY: milking and feeding agribot
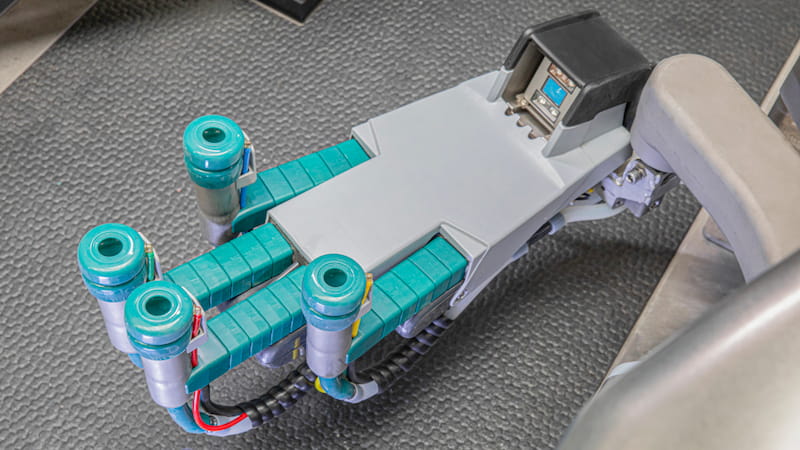
- GEA: robot farm performs every step of the milking process of cows.
Agribot for the management of fully automatic greenhouses.
- SANANBIO: simple solutions for complex vertical farming with robot.
- iFarm: agribot in indoor farming systems for growing crops cost-effectively.
Challenges for robotics in agriculture of the future
The use of robots in agriculture presents some challenges. The agricultural environment cannot be circumscribed, which means that the use of AI must be optimized to manage the multiple sensors present and identify obstacles, as in the case of autonomous driving which takes place thanks to a large amount of data collected and can require a lot of time and resources.
Furthermore, the use of machines drastically reduces the diversity of insect life, microbial life and flora and fauna, which are important variables for the proper functioning of the ecosystem.
Despite this, robotic agriculture offers many opportunities to support the environment and the growing demand for food.
AG Tech could help farmers adapt to a changing climate and restore biodiversity rather than threaten it.

From an economic point of view, the high cost of developing and implementing Agribots and Artificial Intelligence represents a significant obstacle for many small and medium-sized farmers.
Furthermore, the return on investment for agricultural automation can be difficult to calculate, as it depends on many factors, such as crop yields, labor costs and market prices.
You can do a quick ROI calculation for any robot with these tools.
On the other hand, agriculture is one of the oldest and most important activities of humanity, but also one of the most exposed to challenges and problems.
The shortage of skilled labour, the high costs of production factors, the need for environmental sustainability and the growing demand for quality food are just some of the difficulties farmers have to face every day.
To overcome all these challenges, it is crucial to develop scalable and cost-effective AI-powered robots suited to the needs of farmers.
Open source projects, Agribot ROS
Using ROS in agriculture it is possible to reduce the costs of implementing robots and to have customized applications for the type of crop, land or area.
Some examples are:
- ROS in Agricultural Domain

- FarmBot: Open-Source CNC robot farming
- ROS Simulation of Crop Row
Will Agribots steal our jobs?
The Fourth Agricultural Revolution could have a significant impact on human workers.
At best, robotic innovation may simply not be necessary, because small-scale farms with abundant human labor can be both highly productive and rich in biodiversity.
In the worst-case scenario, agriculture could exacerbate the socioeconomic problems already present in agriculture and technology-related industries today.
In the agricultural future, robotic innovation offers the potential to improve the lives of human workers.
A harmonious balance between automation and human labor can increase production efficiency and ensure a better distribution of opportunities in the agricultural sector.
Conclusion
Looking to the future, robotic agriculture promises to revolutionize the agricultural sector with greater efficiency, sustainability and productivity.
Collaboration between developers, farmers and institutions will be crucial to make agricultural automation accessible and adaptable to different needs.
With attention to sustainability and due consideration for social and economic impacts, we can shape a future where Agribots and artificial intelligence will help cultivate a better world.
To know more
Agribot Chat AI: agriGPT to talk about agriculture
Agribot Fairs:
Agribot Podcast:
- AgTech – So What?
- Talking AgTech
- 4AR – Fourth Agricultural Revolution
Agribot Book:
- “Robots in Agriculture: Applications and Economic Viability” by Simon Blackmore, José L. García-Torres and Matthew R. Goddard
A book that explores the applications of robots in agriculture, including the economic challenges and opportunities. - “Automation: The Future of Weed Control in Cropping Systems” by Stephen Powles and Ian Heap
A book examining automation in weed control, including robotic technologies. - “Robotics and Autonomous Systems in Agriculture” by Qin Zhang
A book that explores robotic and autonomous technologies in agriculture, including applications in planting, harvesting and land management. - “Robotics and Automation in Agriculture” by Tsutomu Hashimoto and Gui Yeping
A book that explores robotics and automation technologies in agriculture, including applications in irrigation, harvesting and livestock management systems.
Agribot Blog: Agtecher
Agribot Research:





0 Comments